1 华东师范大学精密光谱科学与技术国家重点实验室,上海 200062
2 华东师范大学重庆研究院,重庆 401120
3 济南量子技术研究院,山东 济南 250101
近年来,智能光子学领域取得了蓬勃发展。其中,机器学习算法与超快光学的结合展现出了巨大潜力,不仅给超快光学系统带来了新功能,也极大地提升了系统的性能。特别地,机器学习已在锁模激光器中获得了广泛应用。本文着重介绍机器学习算法及控制系统在超快光纤激光器中的应用,包括产生和操控孤子锁模脉冲、时空锁模脉冲、呼吸子脉冲以及分形呼吸子。
激光器 锁模 孤子 呼吸子 智能 中国激光
2023, 50(11): 1101006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Chongqing Institute of East China Normal University, Chongqing 401147, China
3 Jinan Institute of Quantum Technology, Jinan 250101, China
In this paper, we demonstrated a series of short-living mode-locking (ML) states (each lasting a few to a hundred microseconds) that happened before a fiber laser reached a steady ML state. With time-stretched dispersion Fourier transform spectroscopy, a rich diversity of transient multi-pulse dynamics were revealed spectrally and temporally. As a result, we found that the formation of the short-living ML states was related to abundant pump power, and their decaying evolution dynamics were possibly governed by gain depletion and recovery. Our results revealed unexpected transient lasing behaviors of a soliton laser and thus might be useful to understand the complex dynamics of mode-locked lasers.
mode-locking soliton fiber laser Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(7): 071401
1 华东师范大学精密光谱科学与技术国家重点实验室, 上海 200062
2 华东师范大学重庆研究院, 重庆 401120
3 济南量子科学研究院, 山东 济南 250101
锁模激光器除了可以产生稳定的超短脉冲以外,还可产生一系列重要的非平衡态动力学过程。这些快速变化的动力学过程有助于理解超快激光器和相关非线性系统的动力学,也对超快激光器的稳定性设计有重要指导意义。随着超快探测技术的发展,锁模激光器超快动力学的研究取得了一系列突破。介绍了锁模激光器几个典型的非平衡态动力学过程,包括锁模启动过程,孤子分子动力学,呼吸子超快激光,以及孤子、呼吸子爆炸动力学。这些研究不仅揭示了超快激光器中新的物理机制,也将进一步促进超快激光器、孤子及呼吸子相关理论的发展。
激光光学 锁模 孤子 呼吸子
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 East China Normal University, State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, Shanghai, China
2 Chongqing Institute of East China Normal University, Chongqing, China
3 Jinan Institute of Quantum Technology, Jinan, China
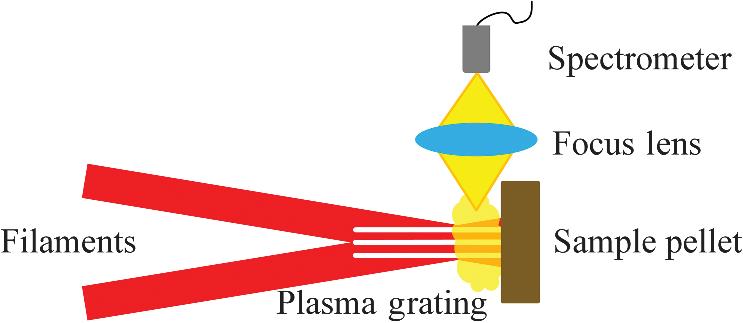
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a useful tool for determination of elements in solids, liquids, and gases. For nanosecond LIBS (ns-LIBS), the plasma shielding effect limits its reproducibility, repeatability, and signal-to-noise ratios. Although femtosecond laser filament induced breakdown spectroscopy (FIBS) has no plasma shielding effects, the power density clamping inside the filaments limits the measurement sensitivity. We propose and demonstrate plasma-grating-induced breakdown spectroscopy (GIBS). The technique relies on a plasma excitation source—a plasma grating generated by the interference of two noncollinear femtosecond filaments. We demonstrate that GIBS can overcome the limitations of standard techniques such as ns-LIBS and FIBS. Signal intensity enhancement with GIBS is observed to be greater than 3 times that of FIBS. The matrix effect is also significantly reduced with GIBS, by virtue of the high power and electron density of the plasma grating, demonstrating great potential for analyzing samples with complex matrix.
femtosecond filament plasma grating induced breakdown spectroscopy high power and electron density enhancement matrix effect Advanced Photonics
2020, 2(6): 065001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Modern Optical System, and Engineering Research Center of Optical Instrument and System, Ministry of Education, School of Optical Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
We report on environmentally stable long-cavity ultrashort erbium-doped fiber lasers, which self-start mode-locking at quite low thresholds by using spectrally filtered and phase-biased nonlinear amplifying long-loop mirrors. By employing 100-m polarization-maintaining fiber (PMF) in the nonlinear loop, the fundamental repetition rate reaches 1.84 MHz and no practical limitation is found to further decrease the repetition rate. The filter used in the long loop not only suppresses Kelly sidebands of the solitons, but also eliminates the amplified spontaneous emission which exists widely in low-repetition-rate ultrafast fiber lasers. The bandwidth of the filter is optimized by using a numerical model. The laser emits approximately 3-ps pulses with an energy of 17.4 pJ, which is further boosted to $1.5~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{J}$ by using a fiber amplifier.
erbium fibers fiber lasers fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators mode-locked lasers High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2019, 7(3): 03000e47





